Curtain Wall
 left click
[right click]
left click
[right click]
- Insert a Curtain wall
- Curtain wall: from curves
- Curtain wall: from surfaces
- Control points
- Insert options and parameters
Insert a Curtain wall
After running the vaCurtainWall command, the curtain wall insert dialog box will appear. This dialog box shows a list of all object parameters and a preview in 2D and 3D of the style selected.
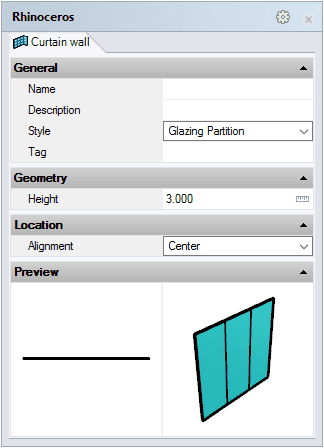
Curtain Wall insert dialog box
Steps:
- Select the curtain wall style you wish to use and define the basic insertion options.
- Select the curtain wall start point (insertion point) with a left-click. When you specify the start point, a dynamic dimension will display the length value of the curtain wall being inserted in real time.
- Left-click again to specify the curtain wall end point.
The length and direction of the curtain wall can be specified as follows:
- Entering the coordinates (relative and absolute) in the command line.
- Entering the value to specify the length and/or angle in the command line.
- Manually, by left-clicking the desired point.
Each new curtain wall will be drawn next to the previous one until you press ENTER, ESC or right click. The command immediately prompts the start point to start drawing the next curtain wall, but it does not link it to the previous curtain wall by default but rather starts drawing it on the new start point selected.
Curtain Wall: From Curves
Curtain walls can be also created from previously drawn curves in the model.
When you run the vaCurtainWall command, the curtain wall insert dialog box will appear.
Steps:
- Select FromCurves in the command line.
- Pick a Curve or multiple Curves from the model that will be used to generate curtain walls. The curves can be any type or shape, as long as they are flat. If a polyline curve is selected, a curtain wall object will be generated for each polyline segment.
- Select the curtain wall insertion options from the
curtain wall
insert dialog box
that will define the curtain wall created from that curve. This
step can be done before or after selecting the curve or curves to
generate curtain walls.
The curtain walls created with this operation behave as all other VisualARQ curtain walls.
Curtain walls created from a polyline generate an individual Curtain wall for each polyline segment.
When two curtain walls have one of their end points in the same position, their horizontal frame component solve their intersection.
Curtain Wall: From Surfaces
Curtain walls can be also created from previously drawn curves in the model.
When you run the vaCurtainWall command, the curtain wall insert dialog box will appear.
Steps:
- Select FromSurfaces in the command line.
- Pick a Surface or multiple Surfaces from the model that will be used to generate curtain walls.
- Select the curtain wall insertion options from the
curtain wall insert dialog box
that will define the curtain wall created from that surface. This
step can be done before or after selecting the surface or surfaces to
generate curtain walls.
The curtain walls created from surfaces behave as all other VisualARQ curtain walls.
NoteCurtain walls can't be created from surfaces laying on the World horizontal planes. Also, curved surfaces may produce imprecise results.
Control Points 
Curtain walls have different control points and control arrows:
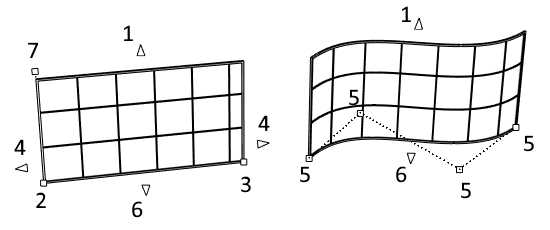
Control points on Curtain walls
- Start control point: defines the curtain wall insertion point. Once the curtain wall is inserted, this control point is used to stretch and/or change the curtain wall direction.
- Control arrow upwards (vertical): used to change the height of the curtain wall. (It is not editable in Top viewport).
- End control point: defines the direction of the curtain wall. It is used to stretch and/or change the curtain wall direction.
- Control arrows (horizontal): used to stretch the curtain wall horizontally from its ends. This control arrow is not available for curtain walls created from curves with a higher degree than 1.
- Curtain wall from curve control points: used to modify the path of curtain walls created from curves.
- Control arrow downwards (vertical): used to change the curtain wall path position. (It is not editable in Top viewport).
- Start top control point: used to move the top horizontal edge and lean the curtain wall (only available on curtain walls with straight paths).
Control points on this object are enabled in the same way as on any other object in Rhino. More details.
- Use the vaProperties command, then select a curtain wall and press Enter, or
- Click on
 ,
then select a curtain wall and press Enter, or
,
then select a curtain wall and press Enter, or - Select a curtain wall and open the context menu by pressing the right mouse button for a while then select Curtain Wall > Properties, or,
- Double click on a curtain wall object.
Insertion Options and Parameters
All the curtain wall insertion options and parameters can be edited in the Object Properties
dialog box  or in the VisualARQ Properties section (in Rhino Properties
Panel
or in the VisualARQ Properties section (in Rhino Properties
Panel  ).
).
General
- Type: curtain wall.
- Name: a field to distinguish the curtain wall from other curtain walls.
- Description: a field for custom notes.
- Style: list of curtain wall styles available in the document.
- Tag: reference text that appears in the tag object.
Display
Isocurves and Plan visibility settings for the curtain wall display in 3D and plan views.
Geometry
- Volume, Area, Length and Thickness. Calculated measurements of the curtain wall. (The area is measured from the vertical surface of the curtain wall, located on its central axis, regardless of the object's alignment).
- Height: even though Height is a curtain wall style property, you can assign a value that is different to the default height value in the insert dialog box.
Location
- Path Curve: change the curtain wall path from the Curve icon
 or change the Start and End points from the Point icons
or change the Start and End points from the Point icons  .
The curtain wall path can be also edited using its own control points.
.
The curtain wall path can be also edited using its own control points.
- Elevation: curtain wall position in relation to the World Z coordinate. (The elevation is always measured on the lowest point of the curtain wall path.)
- Alignment: there are three options to align the curtain wall, depending on
its position based on the direction of its base curve:

Center 
Right 
Left
- Alignment offset: inserts the curtain wall at a specific distance from the direction of its base curve.


 left click
left click
 left click
left click