Beam
 left click
[right click]
left click
[right click]
- Insert a Beam
- Beam: from curves
- Control points
- Insert options and parameters
- Intersections with other objects
Insert a Beam
After running the vaBeam command, the beam insert dialog box will appear. This dialog box shows a list of all object parameters and a preview in 2D and 3D of the style selected.
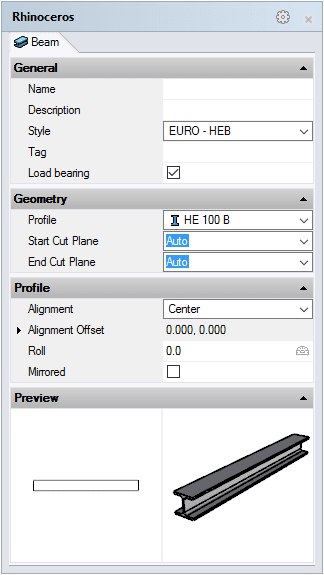
Beam Insert dialog box
Steps:
- Select the Beam style you wish to use and define the basic insertion options.
- Select the Beam start point with a left-click on the desired point.
- Specify the Beam end point with a left-click on the desired point.
Each new beam will be drawn next to the previous one until you press ENTER, ESC or right click. The command immediately prompts the start point to start drawing the next beam, but it does not link it to the previous beam by default but rather starts drawing it on the new start point selected.
You can enter as many beams as you wish and you can cancel the command by pressing ENTER or ESC.
When two beams have one of their end points in the same position, they solve their intersection.
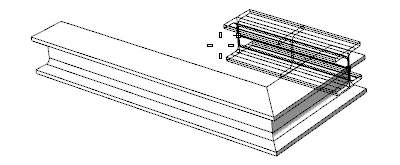
Inserting beams
Beam From Curve
Beams can also be created from a curve in the model:
Steps:
- Start the vaBeam command to create a new beam. The Beam insert dialog box will appear.
- Select the Beam style you wish to use and define the basic insertion options.
- Select FromCurves in the command line and then pick a Curve from the model.
- Press ENTER or right click to finish the command.
Beams created from a polyline generate an individual beam for each polyline segment.
Control Points 
Beams can have different control points depending on how the beam has been created. These control points can be moved in any direction, and modify the beam position and dimensions.
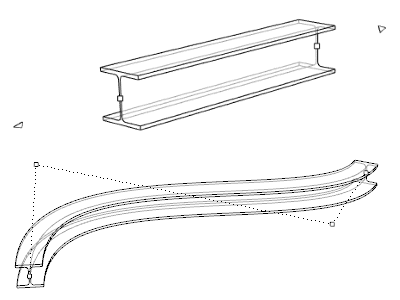
Beam created from a curve, with control points on.
Control points on this object are enabled in the same way as on any other object in Rhino. More details.
- Straight beam: the beam has two control points and two extension arrows at the ends of the object. The control points move the ends of the beams to any position while the extension arrows stretch the beam along its path direction.
- Beam from curve: the beam has as many control points as the curve from which it was created.
- Use the vaProperties command, then select a Beam and press Enter, or
- Click on
 ,
then select a Beam and press Enter, or
,
then select a Beam and press Enter, or - Select a Beam and open the context menu by pressing the right mouse button for a while then select Beam > Properties, or,
- Double click on a Beam object.
Insertion Options and Parameters
All the beam insertion options and parameters can be edited in the Object Properties
dialog box  or in the VisualARQ Properties section (in Rhino Properties
Panel
or in the VisualARQ Properties section (in Rhino Properties
Panel  ).
).
General
- Type: beam.
- Name: a field to distinguish the beam from other beams.
- Description: a field for custom notes.
- Style: list of beam styles available in the document.
- Tag: reference text that appears in the tag object.
- Load bearing: indicates whether the beam performs a structural function or not. This property determines how beams intersect with other objects.
Display
Isocurves and Plan visibility settings for the beam display in 3D and plan views.
Geometry
- Beam calculated measurements: volume, length and cut length.
- Length: length measured from the beam axis.
- Cut Length: length measured from the beam maximum cut size.
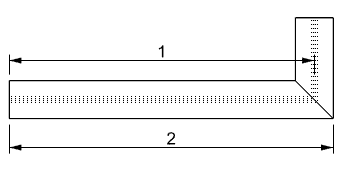
Beam Length and Cut Length
- Profile: shows a list of predefined profiles stored at the beam style. When the profile is set to Other, you can define new values for the profile shape of the selected style.
- Start and End Cut Plane: determine the cut angle of beams at their ends:
- Vertical
- Horizontal
- Perpendicular
- Auto: set this value to calculate beam joints.
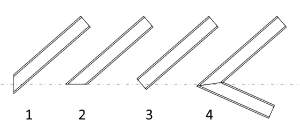
Beam Cut Planes at the start
Location
- Path Curve: change the beam path from the Curve icon
 or change the Start and End points from the Point icons
or change the Start and End points from the Point icons  .
The beam path can be also edited using its own control points.
.
The beam path can be also edited using its own control points.
Profile
- Alignment: position of the beam insertion point according to its profile shape:
- Top Left, Top Center and Top Right
- Middle Left, Center and Middle Right
- Bottom Left, Bottom Center and Bottom Right
- Offset: distance from the beam X and Y points to the insertion point.
- Roll: angle by which the beam rotates around its axis, taking as the center of rotation its alignment position.
- Mirrored: when enabled this option changes the beam orientation into its mirror image.
Intersections
- Maximum extension: specifies the maximum distance by which one beam extends from its ends points to the point where it intersects with another beam.
Intersections with other objects
Beams hide the tangent lines with walls, slabs, and roofs automatically when they have the same section styles.

